Choosing the right battery charger for your lithium-ion battery pack is essential for ensuring both safety and longevity. This guide will walk you through the key factors to consider when selecting a charger, helping you decide to protect and make good use of your battery
1. Know Your Battery Pack Specifications
Nominal Voltage: The ternary lithium battery cells have a nominal voltage of 3.7V, but the fully charged voltage is typically 4.2V per cell. The Lithium iron phosphate battery cells have a nominal voltage of 3.2V & fully charged voltage of 3.6V. Make sure you know clearly the specific voltage of your battery pack (e.g., 3.7V, 7.4V, 11.1V).
Capacity (mAh or Ah): The charger should be able to supply enough current to charge the battery pack within an acceptable timeframe. Thus, you need you know the capacity of your battery pack as well.
2. Charger Output Voltage
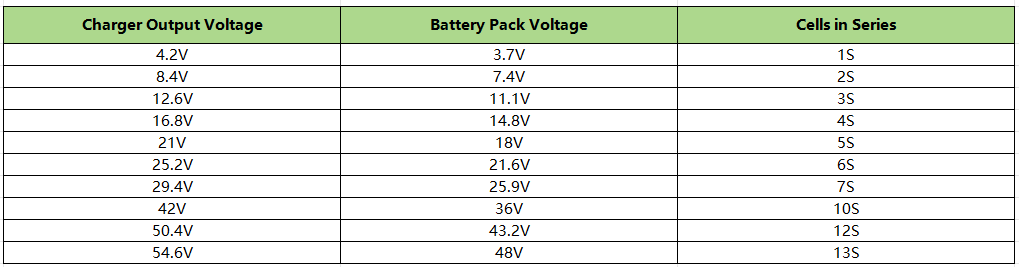
The output voltage of the charger must match the charging voltage of the battery pack. It should be equal to the fully charged voltage of the battery pack. For example, a single 18650 battery cell, its fully charged voltage is 4.2V, so the charger should output 4.2V. When there are 2pcs 18650 battery cells in series, the pack’s fully charged voltage is 8.4V (4.2V x 2), so you will need the charger’s output voltage to be 8.4V. Below is a chart for charger output voltage that is compatible with the battery pack voltages.
3. Charger Output Current
The battery charger current is usually decided by your battery pack BMS. For example, if your BMS is limited to 5A, then you can’t choose the charger current higher than 5A. 2A or 3A will be a good choice for safety considerations. This is a very important part, you need to make sure your battery charger current is well under your BMS’s limited current.
4. Balance Charging (For Multi-Cell Batteries)
If your lithium-ion battery pack has multiple cells in series, the charger should support balance charging. This ensures that each cell is charged to the correct voltage, preventing damage due to unbalanced charging.
5. Safety Protection Functions
Select chargers with safety mechanisms such as overcharge protection, short-circuit protection, and reverse polarity protection to prevent accidents and ensure the longevity of both the charger and the battery.
6. The Charger Materials
The battery charger housing material can be plastic or aluminum, and due to different production methods, the IP ratings are different. Some can be used outside with waterproof function (the shell is sealed), others’ waterproof function may not be good enough that you need to keep it away from water, rain, frogs etc.
By understanding your battery’s specifications, choosing a charger with the proper voltage and current ratings, and prioritizing safety features, you can significantly enhance the lifespan and reliability of your battery. If you still have questions or doubts, please feel free to contact us to discuss.